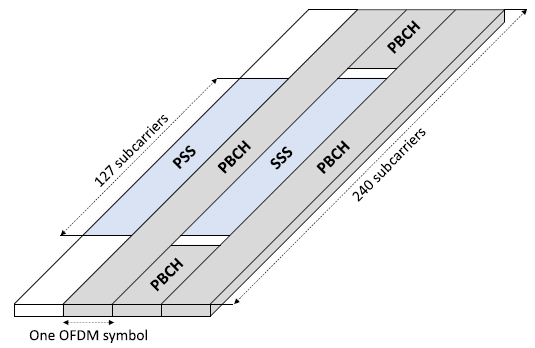
To enable devices to find a cell when entering a system, as well as to find new cells when moving within the system, a synchronization signal consisting of two parts, the Primary Synchronization Signal (PSS) and the Secondary Synchronization Signal (SSS), is periodically transmitted on the downlink from each NR cell.
The PSS/SSS, together with the Physical Broadcast Channel (PBCH), is jointly referred to as a Synchronization Signal Block or SS block
The PSS is transmitted in the first OFDM symbol of the SS block and occupies 127 subcarriers in the frequency domain. The remaining subcarriers are empty.
• The SSS is transmitted in the third OFDM symbol of the SS block and occupies the same set of subcarriers as the PSS. There are eight and nine empty subcarriers on each side of the SSS.
» Read more